Horyu-ji: Japan’s Timeless Temple of Buddhist Heritage
Introduction to Horyu-ji
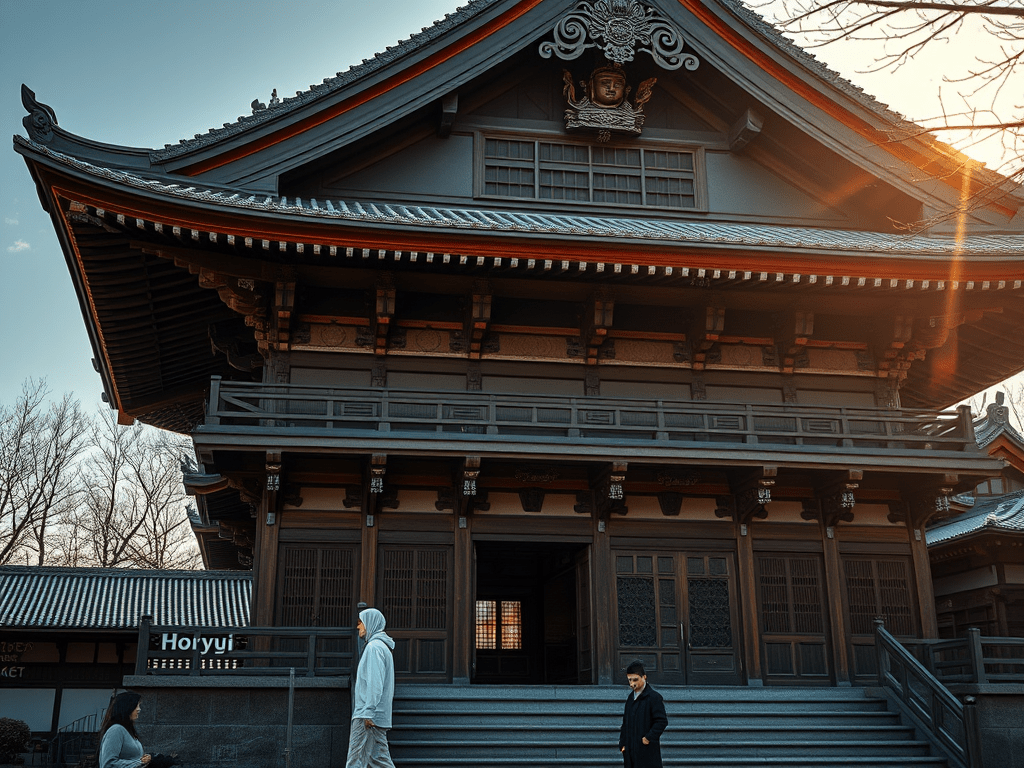
Horyu-ji (法隆寺) is one of Japan’s most revered temples and a UNESCO World Heritage site. Founded in the 7th century, it stands as a testament to early Japanese Buddhist architecture and the profound cultural and religious influence of Buddhism on the nation.
Historical Background
Horyu-ji was established during the Asuka period, a time of significant transformation in Japan as Buddhism began to take root. The temple was commissioned by Prince Shōtoku, a key proponent of Buddhist teachings, and has since become a symbol of Japan’s early embrace of the faith. Over the centuries, Horyu-ji has withstood the test of time, surviving natural disasters and wars, and preserving invaluable cultural treasures.
Architectural Significance
As one of the oldest wooden structures in the world, Horyu-ji is renowned for its unique architectural features:
- Elegant Wooden Construction: The temple complex is celebrated for its sophisticated wooden framework, which exemplifies early Japanese carpentry techniques.
- Artistic Detailing: Intricate carvings, statues, and Buddhist iconography adorn the temple, reflecting the high level of artistry and devotion of its creators.
- Preservation of History: Horyu-ji’s buildings and artifacts offer a rare glimpse into the religious and cultural practices of 7th-century Japan.
Cultural and Religious Impact
Horyu-ji has played a pivotal role in the propagation of Buddhism in Japan. Its influence extends beyond religious practice to the realms of art, education, and philosophy. The temple has been a center for Buddhist scholarship and continues to inspire contemporary art and architecture, symbolizing the enduring legacy of Japan’s spiritual heritage.
Legacy and Modern Relevance
Today, Horyu-ji remains a vital cultural landmark and a popular destination for both pilgrims and tourists. It is celebrated not only as a monument of historical and architectural significance but also as a living repository of Japan’s Buddhist traditions. The temple’s continued preservation and study provide invaluable insights into early Japanese history and the transformative power of religion.