Empress Jitō: The Pioneering Reformer Who Shaped Japan’s Future
Introduction to Empress Jitō
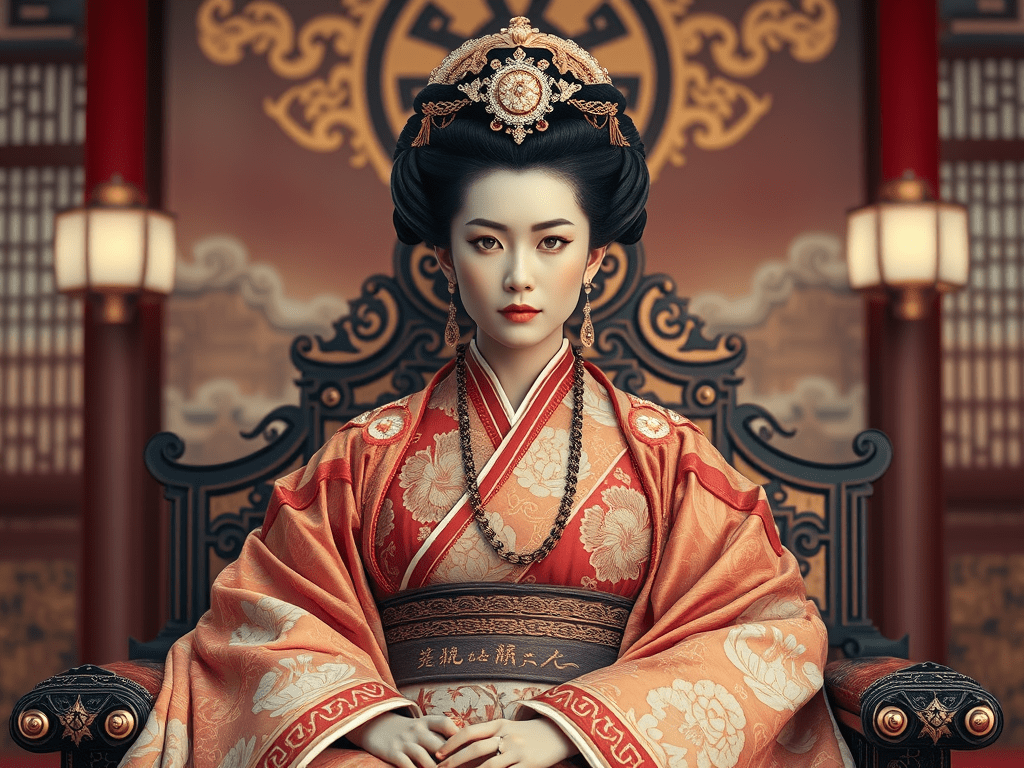
Empress Jitō (持統天皇) was one of the most influential figures in Japan’s early history. As a ruler during the Asuka period, her reign is celebrated for pioneering reforms that helped unify the state and laid the groundwork for Japan’s centralized government.
Historical Background
Empress Jitō ascended to the throne in a time of significant transition. Following a period marked by political strife and regional fragmentation, her leadership brought stability and the integration of various regional powers. Her reign witnessed the consolidation of administrative systems, which was crucial in shaping the future of the Japanese state.
Reforms and Achievements
Empress Jitō’s rule was characterized by a series of groundbreaking reforms:
- Administrative Centralization: She implemented policies that streamlined governance, thereby strengthening the central authority and reducing regional conflicts.
- Land and Tax Reforms: Her efforts in standardizing land distribution and taxation helped ensure a steady revenue stream for the government, fostering economic stability.
- Cultural Integration: Empress Jitō promoted cultural and political exchanges that enriched Japan’s social fabric and advanced its national identity.
Legacy of Empress Jitō
The legacy of Empress Jitō endures as a symbol of visionary leadership and effective governance. Her reforms not only brought unity during a critical period in Japanese history but also set the stage for subsequent developments in law, culture, and administration. Today, she is remembered as a pioneering ruler whose impact resonates in modern Japan.